

Validity is the degree to which a test measures what it is supposed to measure, (Field, 2009). A weakness of this type of test reliability is that it can be difficult to ensure that the two half’s are equal, (Howitt & Cramer, 2011).Īs you can see there are different types of reliability but they all are implemented to test that the consistency of the results, if an experiment provides a significant result, the result needs to be reliable and be consistent over time. It is the extent of which that two of the equivalent versions correlate, (Field, 2009). The Test-Retest method measures the stability of reliability measures between two different points in time an example is of an exam paper by the consistency of the scores of students from two different years when the students took the test at the same age. An example of the internal consistency measure of reliability is the ‘Split Half’ reliability half of the scores should correlate with the other half. If research is reliable the results will be exactly the same or similar if the measurement was taken again. Reliability is addressed in a variety of ways such as- Equivalent Forms, which are most reliable and are used most often an example of this would be exam papers (such as G.C.S.E exams). Reliability in research refers to the consistency of the results which could be at different points of time or in different circumstances, (Howitt & Cramer, 2011). This blog aims to illustrate why it is not and also evaluate the effectiveness of testing Reliability and Validity. Some individuals believe that if something is reliable, it must be valid, this is not true.
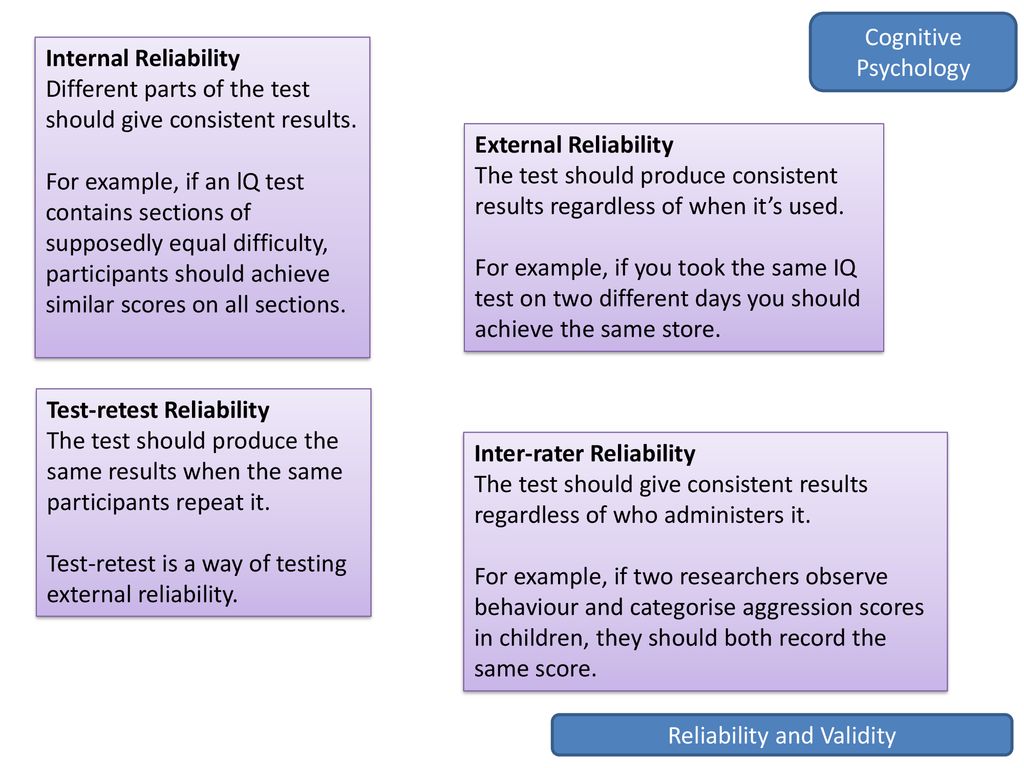
“Reliability and validity are the means by which we evaluate the value of Psychological tests and measures.” (Howitt & Cramer, 2011)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
